NEW Elastic Security 8.16: Elastic AI Assistant knowledge, cloud detection and response, and agentless integrations

Elastic Security 8.16 is now available, advancing our mission to streamline security workflows with enhanced data accessibility and AI-driven analytics. Key updates include agentless onboarding for faster cloud security posture management (CSPM) and asset discovery; expanded integrations with Wiz, AWS Security Hub, and Falco for contextualized threat detection; custom knowledge sources for Elastic AI Assistant; and improved support for locally hosted large language models (LLMs).
These new features deliver practical solutions that improve investigation efficiency and strengthen overall security operations for teams everywhere.
Elastic Security 8.16 is available now on Elastic Cloud — the only hosted Elasticsearch offering to include all of the new features in this latest release. You can also download the Elastic Stack and our cloud orchestration products — Elastic Cloud Enterprise and Elastic Cloud for Kubernetes — for a self-managed experience.
What else is new in Elastic 8.16? Check out the 8.16 announcement blog to learn more.
Elastic AI Assistant adds support for custom knowledge sources
Elastic AI Assistant has already proven valuable in alert investigations, assisting with Elastic Attack Discovery findings, query generation, and much more. Now, it goes further by allowing custom knowledge sources to be added.
This update to Elastic AI Assistant takes interactions to a whole new level. You can now add custom sources to the assistant as additional knowledge. This means you are no longer bound to the knowledge a given LLM is trained on, and you can add knowledge sources beyond what Elastic provides.
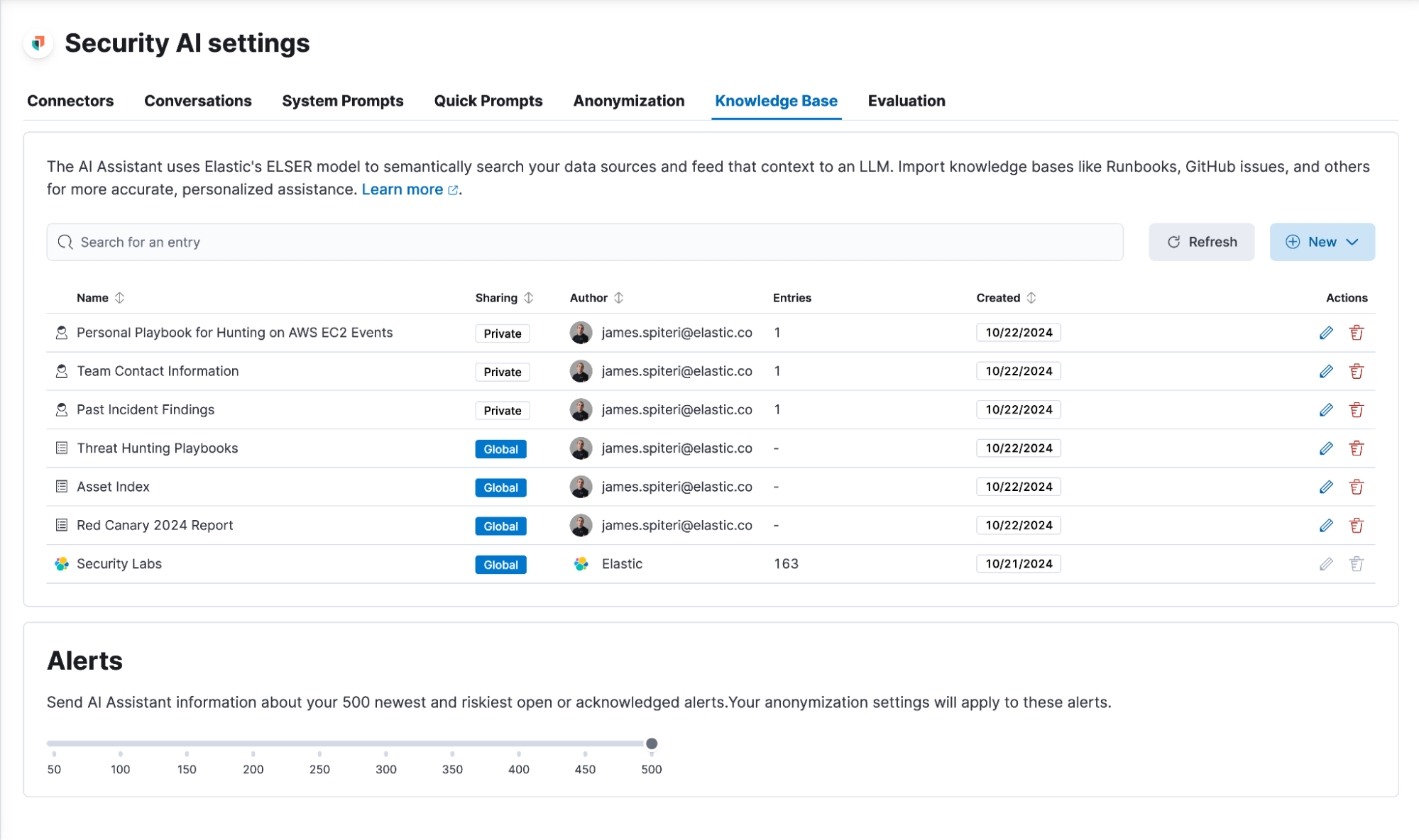
Custom knowledge sources can take the form of a simple text or markdown entry as well as an index that has been configured with a semantic text field. The new knowledge settings user interface makes the process of adding knowledge sources a breeze, allowing you to configure the content and the sharing settings for that knowledge.
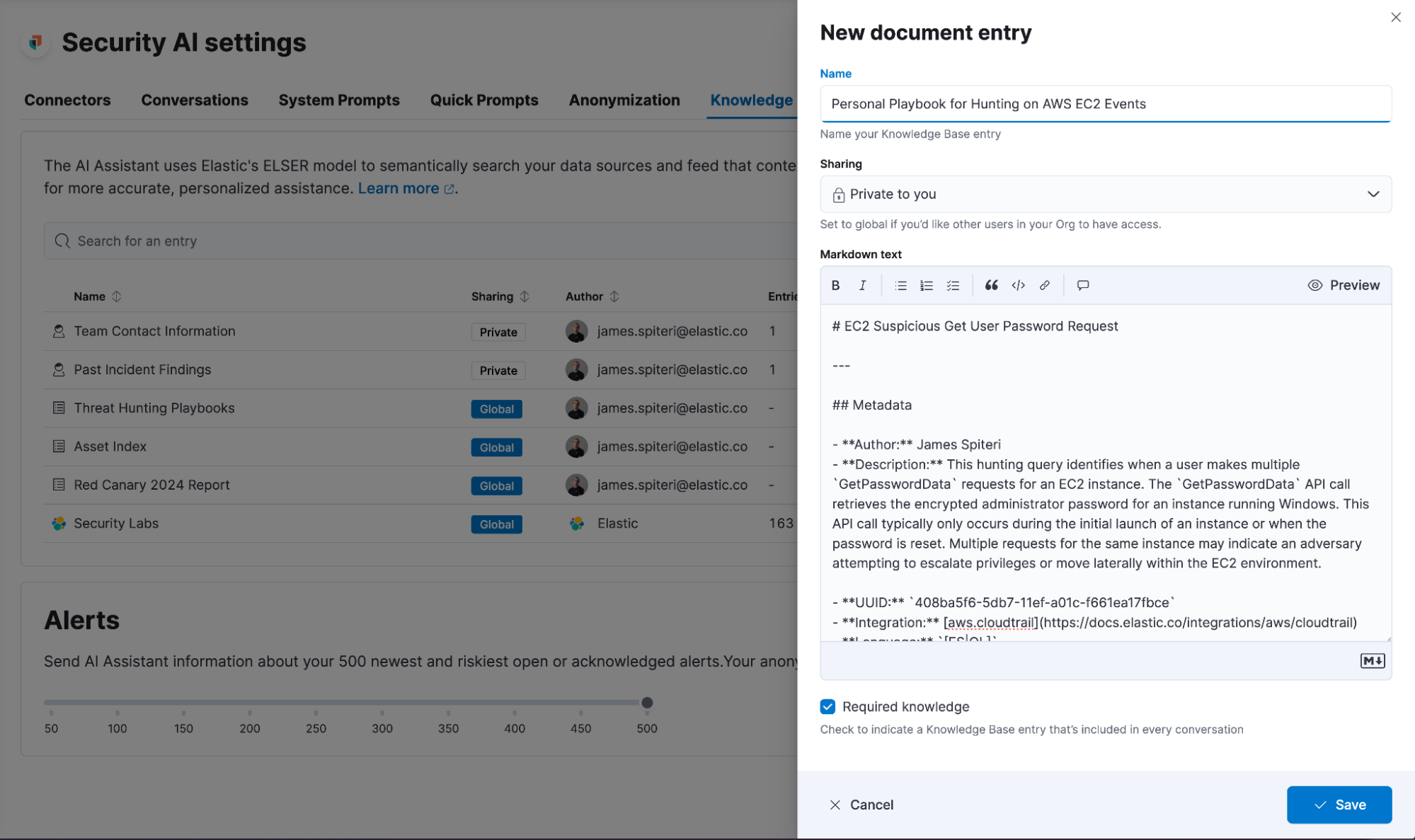
In addition, Elastic AI Assistant can now be asked to remember content as knowledge during a conversation. Simply tell the Elastic AI Assistant what you would like remembered, and it will be available as a custom knowledge source going forward.
Here are some examples of how custom knowledge sources can be used:
Attaching an index containing asset information, such as content found in a configuration management database (CMDB)
Adding your favorite threat intelligence reports to be used during a conversation
Documents containing any existing threat hunting playbooks or standard operating procedures
Historical incident or case information
On-call schedules

Visit the blog on custom knowledge for more information.
Elastic Security Labs content now integrated as an Elastic AI Assistant knowledge source
Elastic Security Labs continuously provides cutting-edge research on emerging threats, including novel malware, advanced threat groups, and detailed analysis of security incidents. This wealth of knowledge is now directly accessible through Elastic AI Assistant for Security. Whether you're responding to an active incident, conducting a threat hunting exercise, or simply looking for a quick summary, the assistant can reference Elastic Security Labs content to offer deeper context and informed insights.
Security teams can use these insights to enhance threat detection and response strategies, ensuring they stay ahead of evolving threats. The Elastic AI Assistant now includes all Elastic Security Labs content published up until September 2024, making it a powerful tool for faster, more informed decision-making in real-time scenarios.

Elastic Attack Discovery now supports higher alert counts, role-based access control, and improved result accuracy
Up until the 8.16 release, Elastic Attack Discovery was able to process and discover attacks by analyzing up to a maximum of 100 alerts. This limit has now been increased to 500 alerts, and we’ve made it easier to configure from within the Elastic Attack Discovery screen itself.
In addition, we’ve made significant improvements to result accuracy, error handling, and have added role-based access control (RBAC) for the feature.

Improved support for locally hosted models
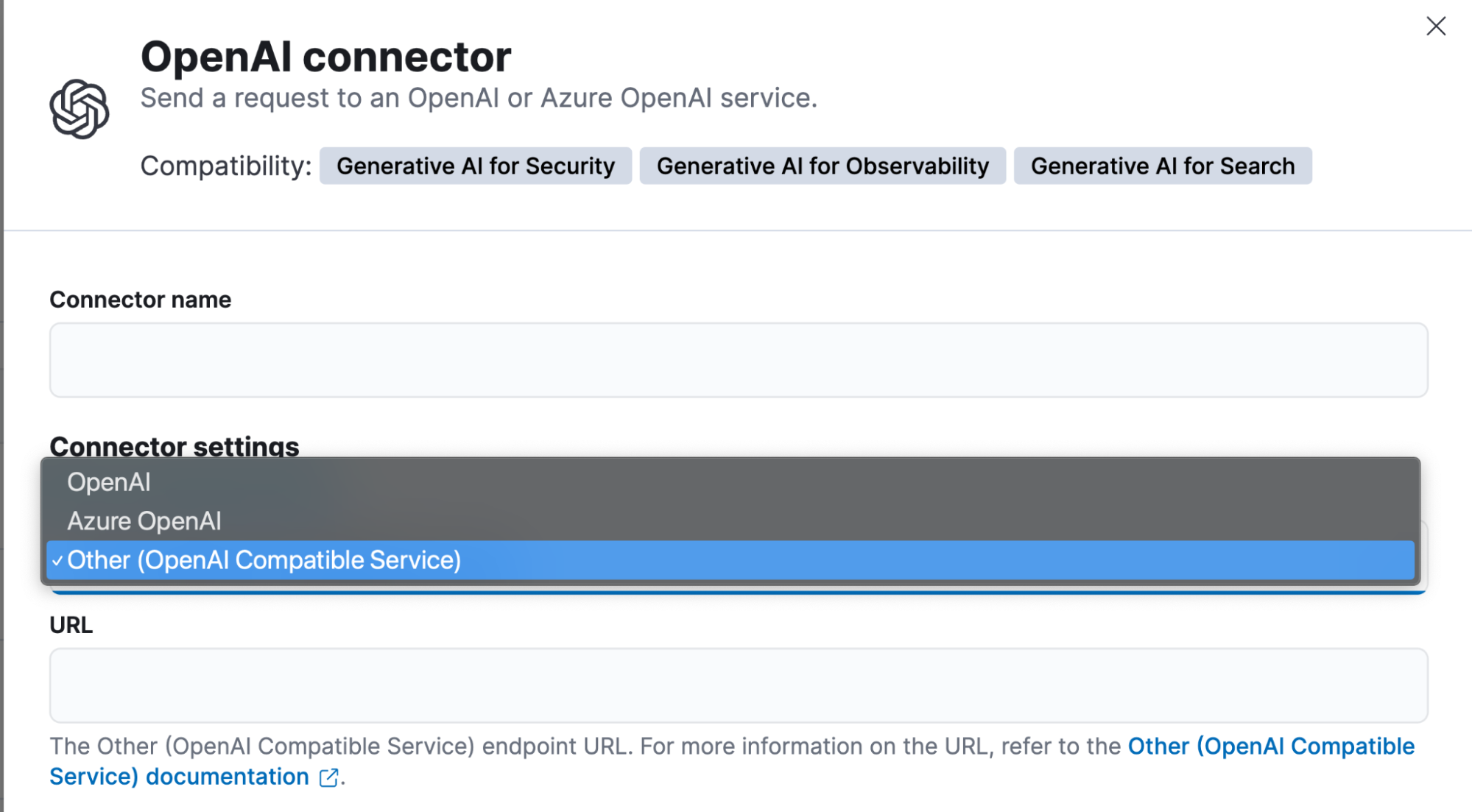
With this release, we’ve made it even easier to use locally hosted LLMs with Elastic AI Assistant and Attack Discovery. The OpenAI connector has been updated to better highlight this capability. We’ve also made significant improvements to the Elastic AI Assistant and Attack Discovery when using locally hosted and open source models.
Elastic Automatic Import expands support for new AI models and log formats
Since its recent debut in the Elastic 8.15 release, Automatic Import now automates the development of custom data integrations — streamlining the custom data onboarding process from hours to just minutes. Now, this feature supports additional AI models such as Amazon Bedrock, OpenAI, and Google Gemini.
Users can also take advantage of expanded log format compatibility, making it easier to parse and normalize various types of logs — from structured to unstructured and CSV formats. This enhancement simplifies data ingestion, enabling users to focus more on analysis and threat detection.
Agentless CSPM and cloud asset inventory management
Elastic Security introduces agentless integration for both CSPM and a new Cloud Asset Inventory, which is currently released in public beta. This new capability removes the need for agents, allowing users to quickly establish trust between their cloud providers — AWS, Azure, or GCP — and Elastic Cloud, speeding up data ingestion to just minutes.
With this option, discovering cloud assets and monitoring security posture becomes more efficient — all without managing agents.
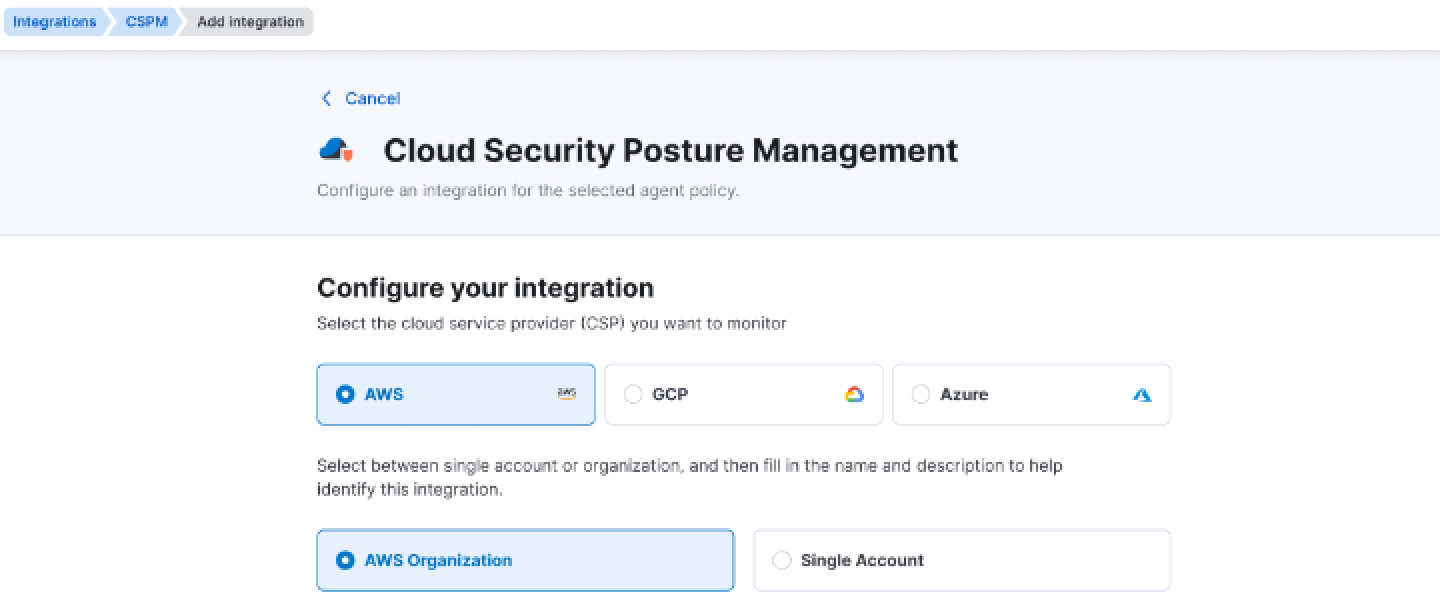
Note: Agent-based integration for CSPM is still available as an alternative.
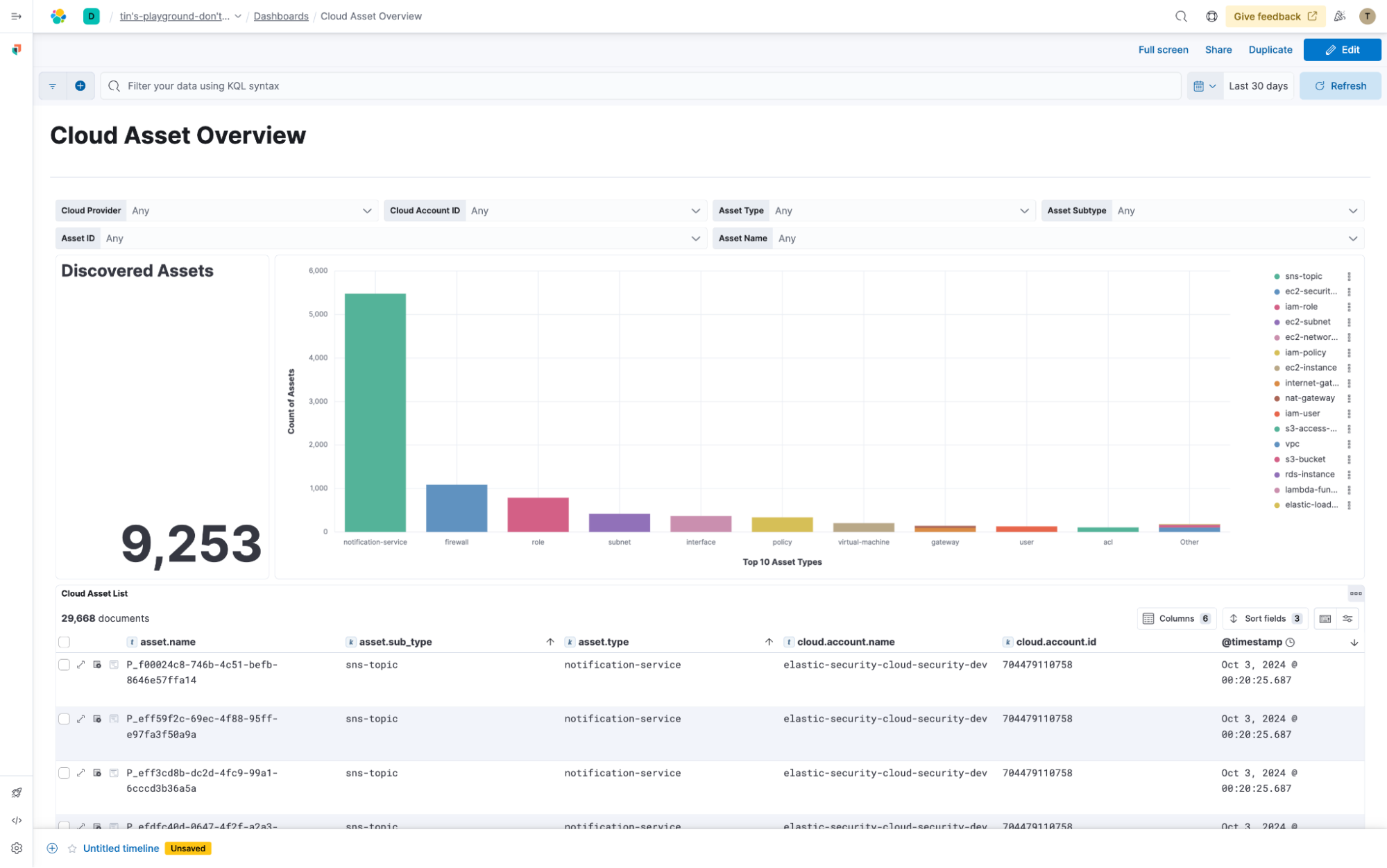
New Cloud Asset Inventory integration in technical preview
You can't protect what you don't know. With the new Elastic Security Cloud Asset Inventory integration, you can discover your cloud resources across AWS, GCP, and Microsoft Azure. By simply connecting your cloud accounts with read-only access, this integration automatically finds your cloud services and assets, including S3 buckets, EC2 instances, Azure Virtual Machines, GCP Compute Engine instances, and more.
With these assets brought into Elastic Security, you can add valuable context to your threat detections and use Elastic's powerful detection engine to craft security and compliance checks over this rich asset metadata. This helps ensure that your cloud environment is properly configured like verifying that multifactor authentication (MFA) is enabled for your cloud users.
Whether you're tracking assets for compliance or investigating security incidents, the Cloud Asset Inventory integration gives you a clear view of your cloud footprint, helping you stay secure.
Contextualized threat detection for Wiz, AWS Security Hub, and Falco data
Elastic Security is also introducing native cloud security workflows for third-party security tools, including CNCF open source tools — enhancing threat detection and investigation. This feature integrates posture and vulnerability findings with runtime security alerts from top vendors like Wiz, AWS Security Hub, and Falco, enabling seamless, out-of-the-box investigations from alerts, hosts, users, and findings workflows.
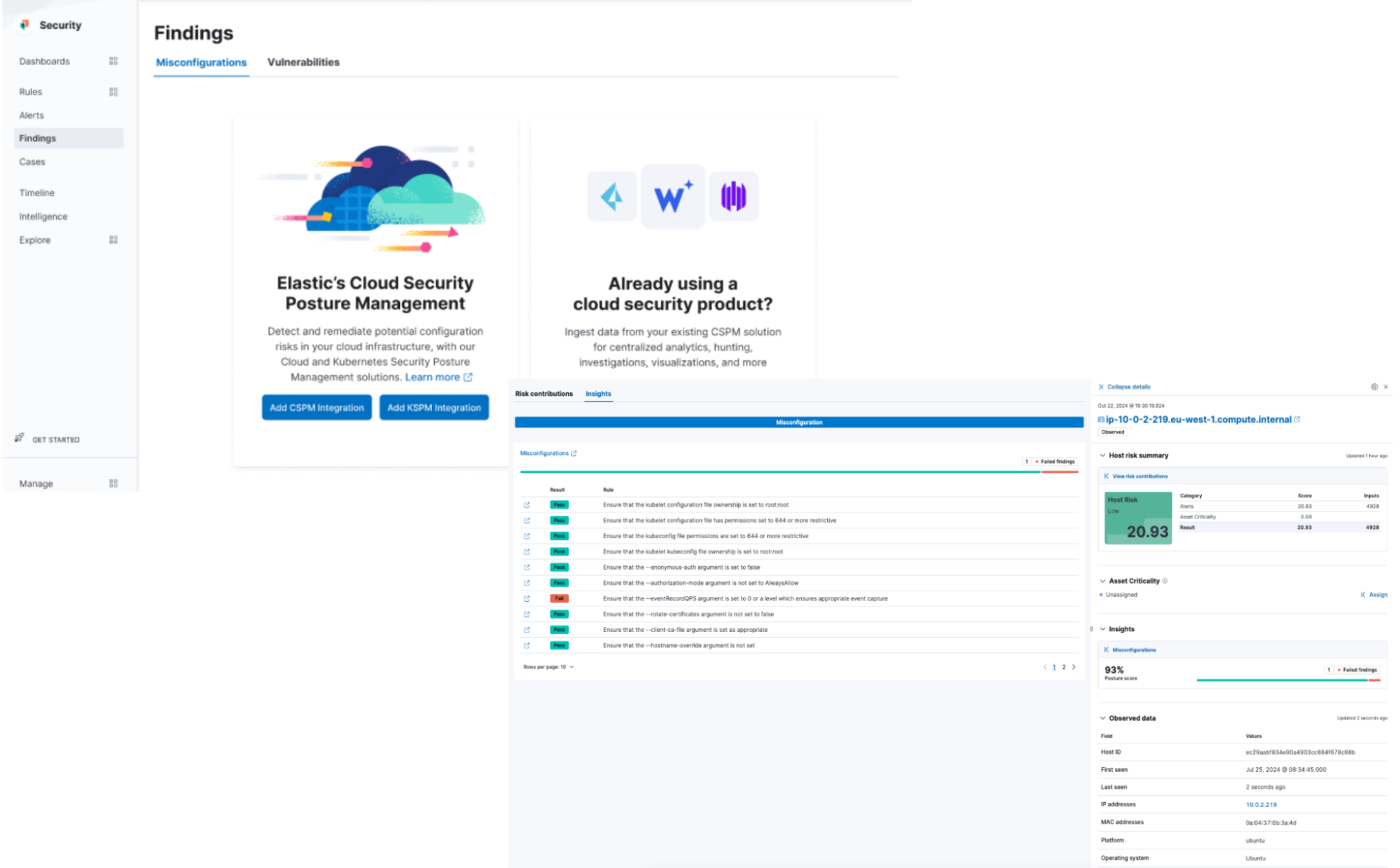
Our focus is to deliver vendor-agnostic workflows, simplifying the investigation process and enhancing productivity for security teams. Dive deeper into the power of this integrated approach in this blog with a scenario-driven example..
We welcome your feedback on which vendors you’d like to see included. Join our community Slack to pass on the inputs to the cloud security product team directly!
Extended session view support for Auditbeat and Auditd Manager
With expanded session view support for Auditbeat and Auditd Manager datastreams, security analysts can now visualize Linux processes in a clear, tree-like structure. This allows for quicker identification of unusual behavior and a more efficient investigation of alerts.
This visual approach to understanding Linux processes reduces the complexity of analyzing system audit logs, providing a more intuitive way to investigate threats and support compliance efforts. The enhanced session view empowers teams to work more efficiently in protecting Linux environments.

Manual rule runs, alert suppression news, and more
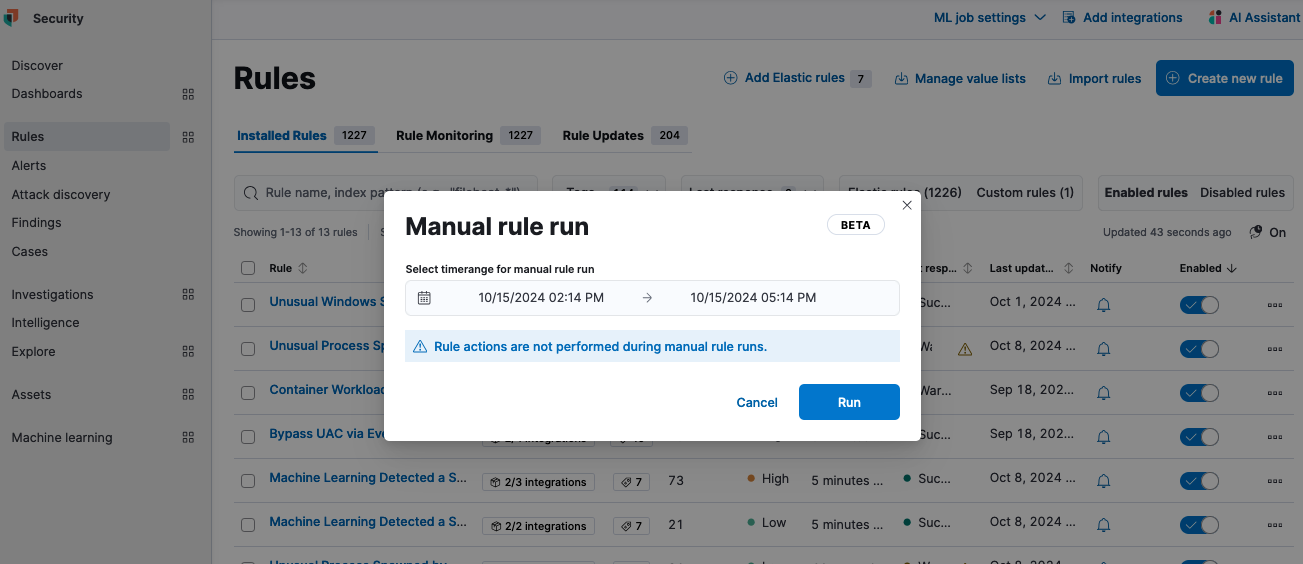
Elastic Security 8.16 brings full alert suppression support for several rule types, helping reduce alert volume and improve triage efficiency. Manual rule runs — now available in beta — allow detection engineers to test or rerun detection rules over selected periods. This functionality helps backfill alerts and assess the effectiveness of new rules against historical data, making it easier to refine detection capabilities.
An additional new feature allows users to create a case directly from Elastic Security, streamlining investigations by aggregating multiple alerts into one case. These tools give security teams the flexibility to test, suppress, and manage alerts in a way that best suits their workflow.
Also, a new option is added to enable the rule at the time of installation. The rule preview functionality is enhanced to show the ES requests your ES|QL or EQL rules will execute.
Expansion of security integrations enhances visibility
Elastic Security continues to expand the integration ecosystem, allowing users to ingest threat intelligence from any API using custom threat intelligence packages. New integrations with Sublime Security and Abnormal Security boost email monitoring capabilities, while Jamf adds deeper insights into the Apple ecosystem.
Network security is further strengthened through partnerships with Fortinet FortiProxy and Palo Alto Prisma Access. Teleport integration also improves access management monitoring — expanding visibility across your organization’s security infrastructure.
TheHive case management integration
A new Hive case connector allows for seamless case creation and management directly from Elastic. Users can configure incident details like severity levels and tags, while maintaining separate status tracking across platforms. The integration supports flexible deployment with proxy and TLS settings that are easily managed via API key authentication.
Enhanced collaboration during investigations
Users can now add notes during their investigative workflows. This feature is introduced within our event and alert detail experiences and allows users to add a comment via markdown. Up until this point, flexible collaboration like this has been limited to the case or timeline workflows. But now, teams can coordinate responses, threat hunt, or share investigative findings within the object directly. This will drastically improve the analyst experience as users will no longer need to keep notes in separate tools.
Try it out
Read about these capabilities and more in the release notes.
Existing Elastic Cloud customers can access many of these features directly from the Elastic Cloud console. Not taking advantage of Elastic on cloud? Start a free trial.
The release and timing of any features or functionality described in this post remain at Elastic's sole discretion. Any features or functionality not currently available may not be delivered on time or at all.
In this blog post, we may have used or referred to third party generative AI tools, which are owned and operated by their respective owners. Elastic does not have any control over the third party tools and we have no responsibility or liability for their content, operation or use, nor for any loss or damage that may arise from your use of such tools. Please exercise caution when using AI tools with personal, sensitive or confidential information. Any data you submit may be used for AI training or other purposes. There is no guarantee that information you provide will be kept secure or confidential. You should familiarize yourself with the privacy practices and terms of use of any generative AI tools prior to use.
Elastic, Elasticsearch, ESRE, Elasticsearch Relevance Engine and associated marks are trademarks, logos or registered trademarks of Elasticsearch N.V. in the United States and other countries. All other company and product names are trademarks, logos or registered trademarks of their respective owners.