Elastic 7.12 released: General availability of schema on read, technical preview of the frozen tier, and support for autoscaling
We are pleased to announce the general availability (GA) of Elastic 7.12. This release brings a broad set of new capabilities to our Elastic Enterprise Search, Observability, and Security solutions, which are built into the Elastic Stack — Elasticsearch and Kibana. This release enables customers to choose between unmatched flexibility and speed with schema on read, unlock new value by making object stores fully searchable with the new frozen tier, and automatically scale deployments on Elastic Cloud.
Elastic Enterprise Search benefits from a number of architectural enhancements that deliver reduced deployment size, faster indexing, and more relevant results. Correlations come to Elastic Observability, helping to identify top drivers of application performance issues and errors. Analyst-driven correlation streamlines SecOps workflows in Elastic Security.
Elastic 7.12 is available now on Elastic Cloud — the only hosted Elasticsearch offering to include all of the new features in this latest release. You can also download the Elastic Stack and our cloud orchestration products, Elastic Cloud Enterprise and Elastic Cloud for Kubernetes, for a self-managed experience.
Read on for the key release highlights. To get the full feature rundown, dive into the individual solution and product blog posts.
Elastic Stack and Elastic Cloud
Let analysts flexibly explore data through schema on read, now generally available.
Elasticsearch is known for being a blazing fast distributed search and analytics engine in part because of schema on write, the default schema for Elasticsearch. This organized structure of data requires planning and testing of how the data will be represented in Elasticsearch, but the big payoff is speed.
What happens when you need to ingest new data or adopt a new use case with a fast turnaround? What if you had the option to create schema on the fly at query time with schema on read? Runtime fields, now generally available, give you the flexibility to define schema on read in addition to using schema on write. This feature greatly reduces the time-to-value with your data by trading off some search performance. With the 7.12 release, runtime fields are now searchable in Kibana Discover, allowing analysts to flexibly explore data structured through schema on read in Elasticsearch.
Our implementation of schema on read is special. With Elasticsearch runtime fields you do not have to choose between the speed and scale of schema on write or the flexibility of schema on read. You can use both at the same time, on the same Elastic Stack, and on the same data. Explore new data and define new fields on the fly while still searching on the fields in the data you already know. Easily shift between the newly created fields, defined in runtime fields, and schema on write for speed and performance. No matter your approach, you have unparalleled flexibility with the speed and scale you come to expect of Elasticsearch.
Unlock new value by making object stores like S3 fully searchable with the new frozen tier, now in technical preview, with a simplified experience in Elastic Cloud coming soon.
With the new frozen tier, now in technical preview, you have the ability to decouple compute from storage, adding the capability to search directly on object storage such as Amazon S3, Google Cloud Storage, and Microsoft Azure Storage. This functionality allows you to search your data at a fraction of the cost with a tradeoff in performance while reducing the amount of dedicated resources needed for search. By fetching only the data needed to complete a query from the object store and caching this data locally as needed, the frozen tier offers the best search experience while enabling you to store an unlimited amount of data. We will also be offering an enhanced user experience for configuring the frozen tier in Elastic Cloud, coming soon.
With searchable snapshots, you can cost-effectively search across all of your application content and historical workplace records without breaking the bank. Store more analytics data for marketing analysis, or test and release versioned application catalogs for new deployment strategies. In observability, you no longer need to choose which log, metric, or APM data to delete to save money. Imagine having the ability to search year over year on application performance without needing to rehydrate your data from backup. For your threat hunters and security analysts, imagine arming them with years of high-volume security data sources made easily accessible through searchable snapshots. Collect additional security-related data — IDS, NetFlow, DNS, PCAP, or endpoint data — at greater scale and keep it accessible for longer.
Stay in the flow of analyzing data while your long-running queries complete on their own with a new “save search to background” feature.
Searching across huge amounts of data in pursuit of the proverbial needle in a haystack is core to what Elastic’s technology helps people do. Even when those results live in data on a frozen index spanning multiple clusters, the Elastic Stack won’t stop combing through documents on your behalf until the job is done. But just because it's going the extra mile doesn’t mean you have to stop what you’re doing. Now with 7.12 you can send long-running search sessions in Discover or on a Kibana dashboard to run in the background while you keep tackling your day. The new search session management interface lets you check back on the results whenever you want, no matter if that’s 5 minutes, 5 hours, or even 5 days later. Let the Elastic Stack do the multitasking so you can stay laser focused on getting things done.
Let Elastic Cloud automatically monitor storage utilization and machine learning capacity, adjust resources, and maintain performance with autoscaling so that you can focus on running your business.
Autoscaling is now available for Elastic Cloud and Elastic Cloud Enterprise 2.9. Autoscaling monitors both the storage utilization for your Elasticsearch data nodes, as well as the available capacity for your machine learning jobs. Autoscaling automatically adjusts resource capacity to maintain node performance.
You can enable autoscaling using the API, CLI, or from the Elastic Cloud console. Your Elasticsearch data nodes’ capacity will grow as you store more data. Your machine learning node’s memory and CPU capacity will grow or shrink based on the resource requirements of your machine learning jobs. You can also set thresholds to prevent runaway cluster growth.
With autoscaling, you can keep up with dynamic observability demands by extending instrumentation to all applications in an optimized fashion without overpaying for max capacity — it’s been one of the Elastic Observability community’s most requested features. In Elastic Enterprise Search, use autoscaling to drive greater insights into your search platform with less overhead, seamlessly scaling with your logs, analytics, and content. In Elastic Security, complete large-scale threat hunting exercises and let autoscaling monitor and grow memory resources for your machine learning nodes as they perform anomaly detection against your security event information.
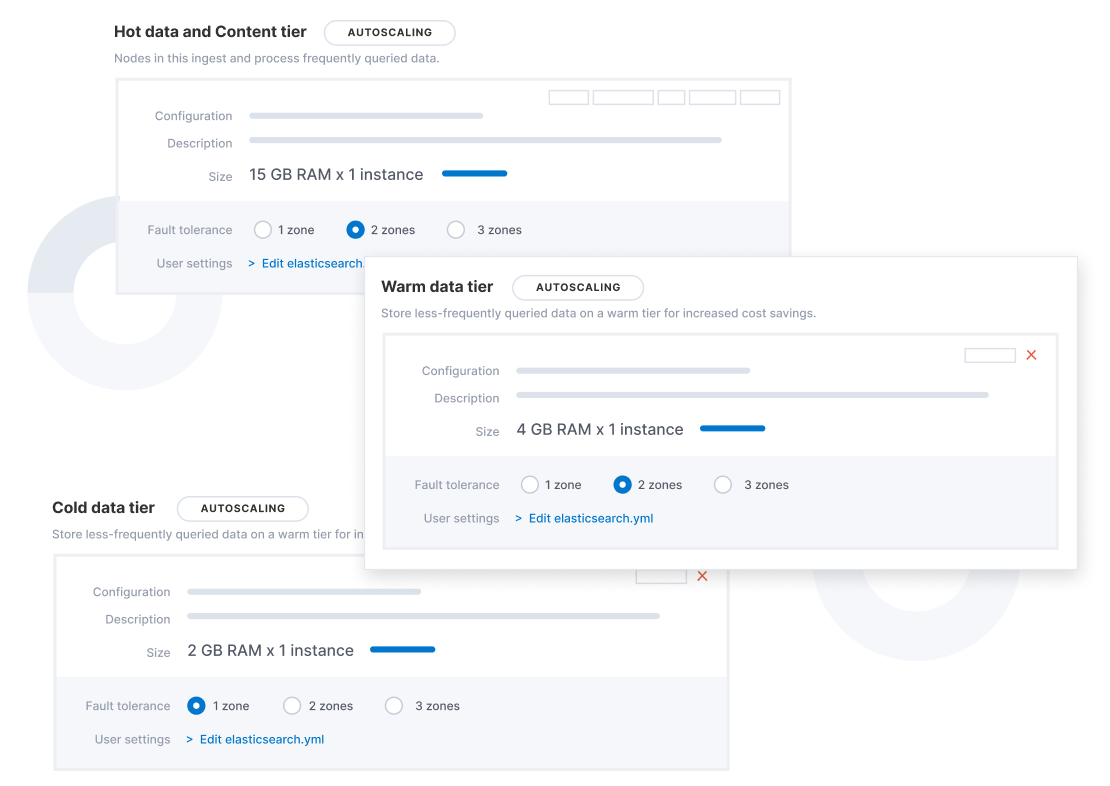
Take advantage of improved flexibility and price/performance with support for new instance types on Elastic Cloud.
Take advantage of Ls-Series instances in the Microsoft Azure London and Tokyo regions. Ls-Series I/O optimized instances feature high throughput and low latency. These instances also deliver a cost savings of more than 55% when compared to the previous E-Series instances. Your deployments will benefit from higher performance and lower costs.
Take advantage of D3 instances in the AWS Ireland, Virginia, Ohio, and Oregon regions. D3 instances provide high-capacity local storage for dense storage workloads while delivering additional performance at a lower cost when compared to D2 instances. With support for ARM now available in the Elastic Stack, we are also working on supporting ARM-based EC2 instances soon. These instances offer significant cost savings and are perfect for deployments with distributed data stores.
Read about these features and more in the Kibana 7.12 blog, the Elasticsearch 7.12 blog, and the Elastic Cloud 7.12 blog.
Elastic Solutions
Elastic Enterprise Search
Drive more value by reducing deployment size, speeding up indexing, and delivering more relevant results.
Elastic pioneered resource-based pricing for search use cases years ago, providing a predictable, transparent, and fair approach to operating search experiences at scale. With the same principles in mind, the Enterprise Search team is constantly looking for ways to optimize resource usage, capacity management, and relevance through research and domain expertise — investing in complex modeling decisions so you don’t have to. That way, all you have to do is enjoy the benefits of a pre-tuned, ready-to-deploy experience.
With the 7.12 release, Elastic Enterprise Search provides a reimagined underlying data architecture that delivers greater storage efficiency, search performance, and relevance. The new architecture optimizes the underlying index management to eliminate data duplication and employs a new mapping configuration that improves search precision while maintaining the typo-tolerance that modern search experiences require. Customers may experience up to 70% improvement in storage efficiency, up to 40% reduction in indexing latency, and significant improvements to relevance across App Search and Workplace Search.
Get a scoop on all of the new Elastic Enterprise Search features in the Elastic Enterprise Search 7.12 blog.
Elastic Observability
Uncover meaningful patterns in slow application transactions and speed up root cause analysis with a new correlation capability in Elastic APM.
Elastic APM introduces a new capability that analyzes application transactions with high latencies and errors and automatically surfaces factors like service version and infrastructure metadata that are highly correlated with those underperforming transactions. With this capability, users can instantly zoom in on the root cause of poor performance during reactive troubleshooting workflows, reducing their mean time to resolution. This capability also drives proactive workflow, helping application owners identify areas of improvement and continually improve the end user experience.
For example, the correlation feature might surface that a particular service version is highly correlated with slow performance, or that a particular customer is overrepresented in transactions with errors. These insights help an engineer narrow in on the next step in their investigation.
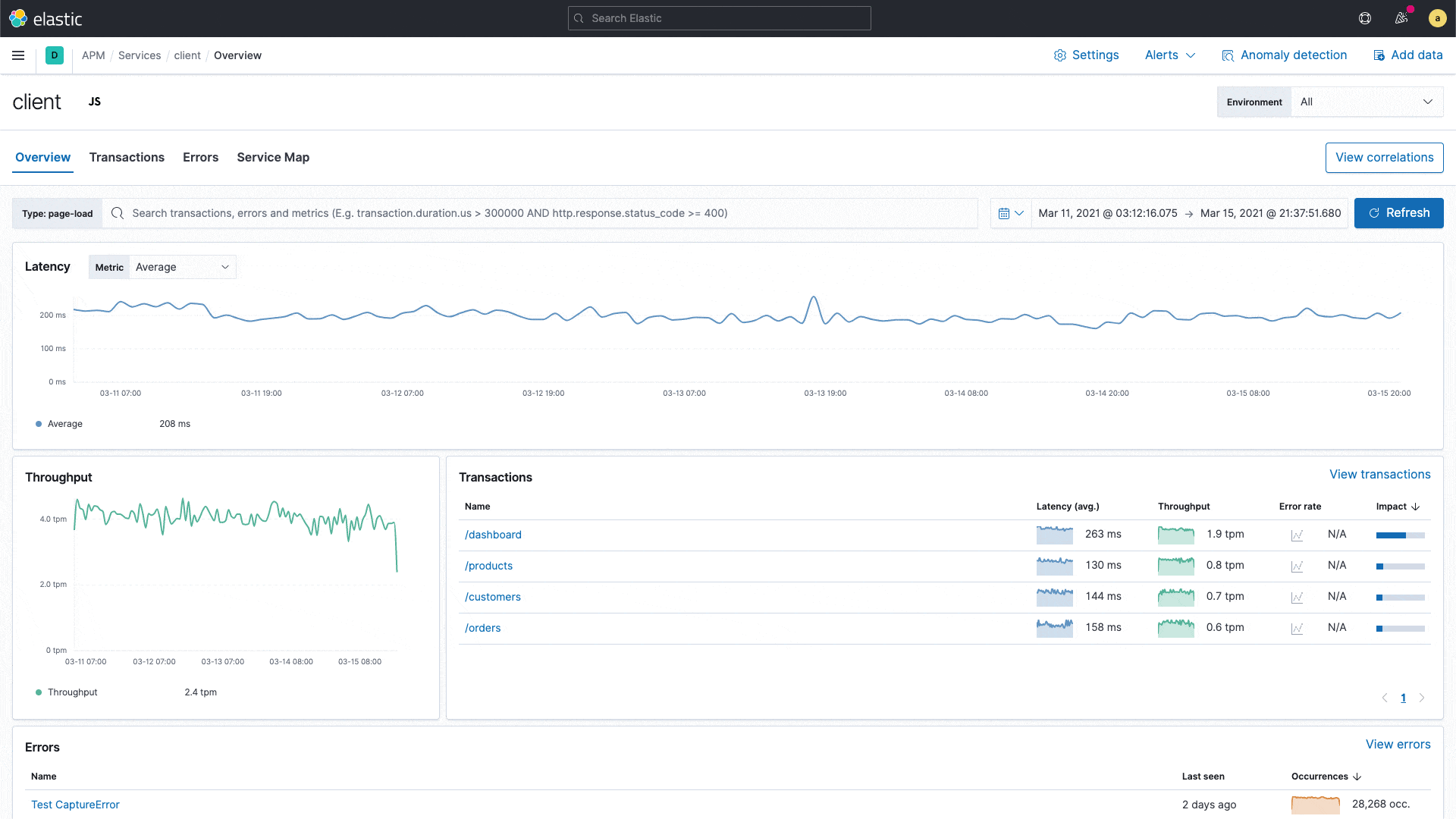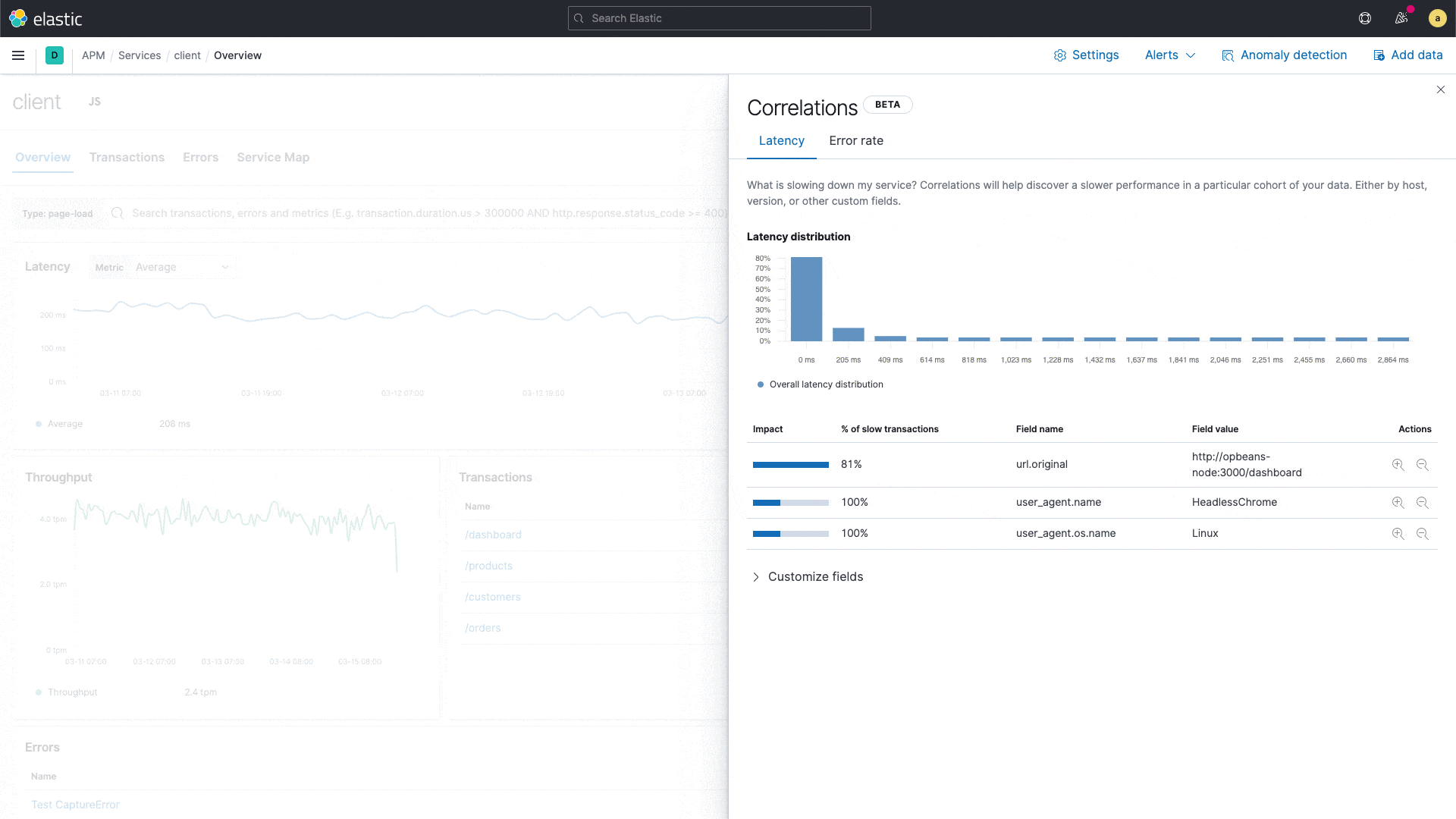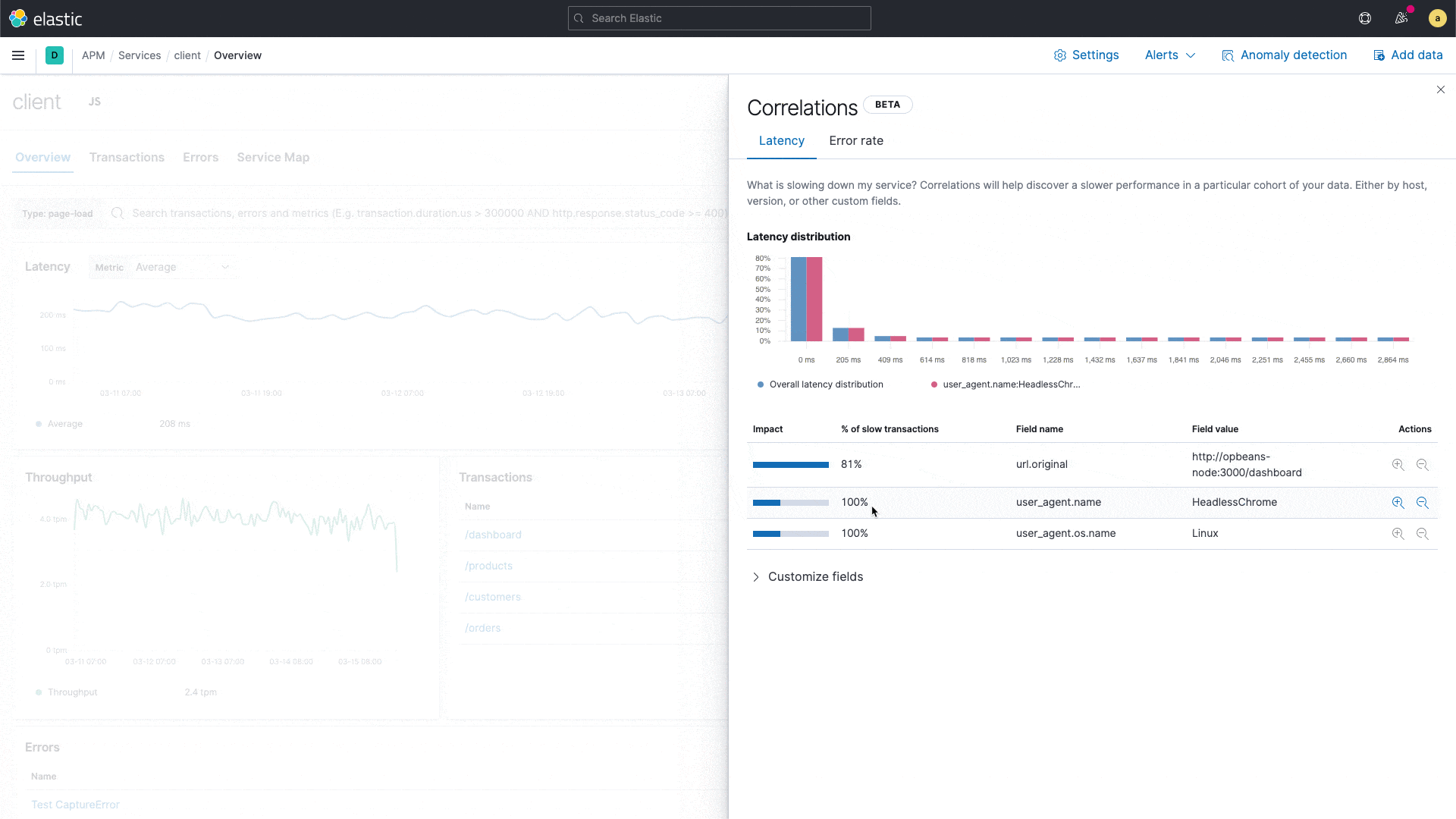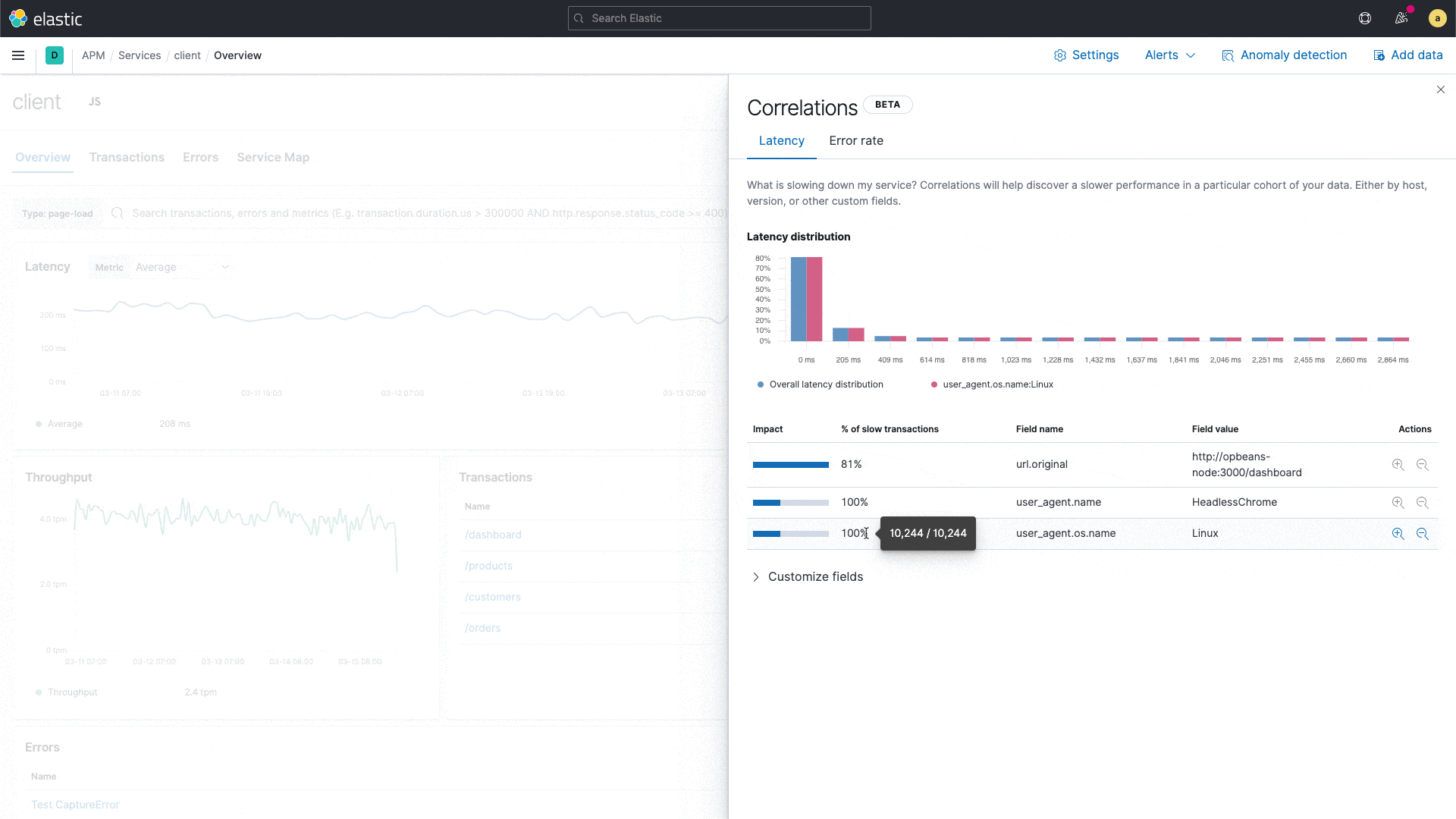
New correlations in Elastic APM
Built on the significant terms aggregation in Elastic, the new correlation feature compares the tags on those transactions with high latencies and errors to the full transaction set, and automatically identifies metadata that is unusually common in suboptimal transactions.
Dive deeper into all the new features in the Elastic Observability 7.12 blog.
Elastic Security
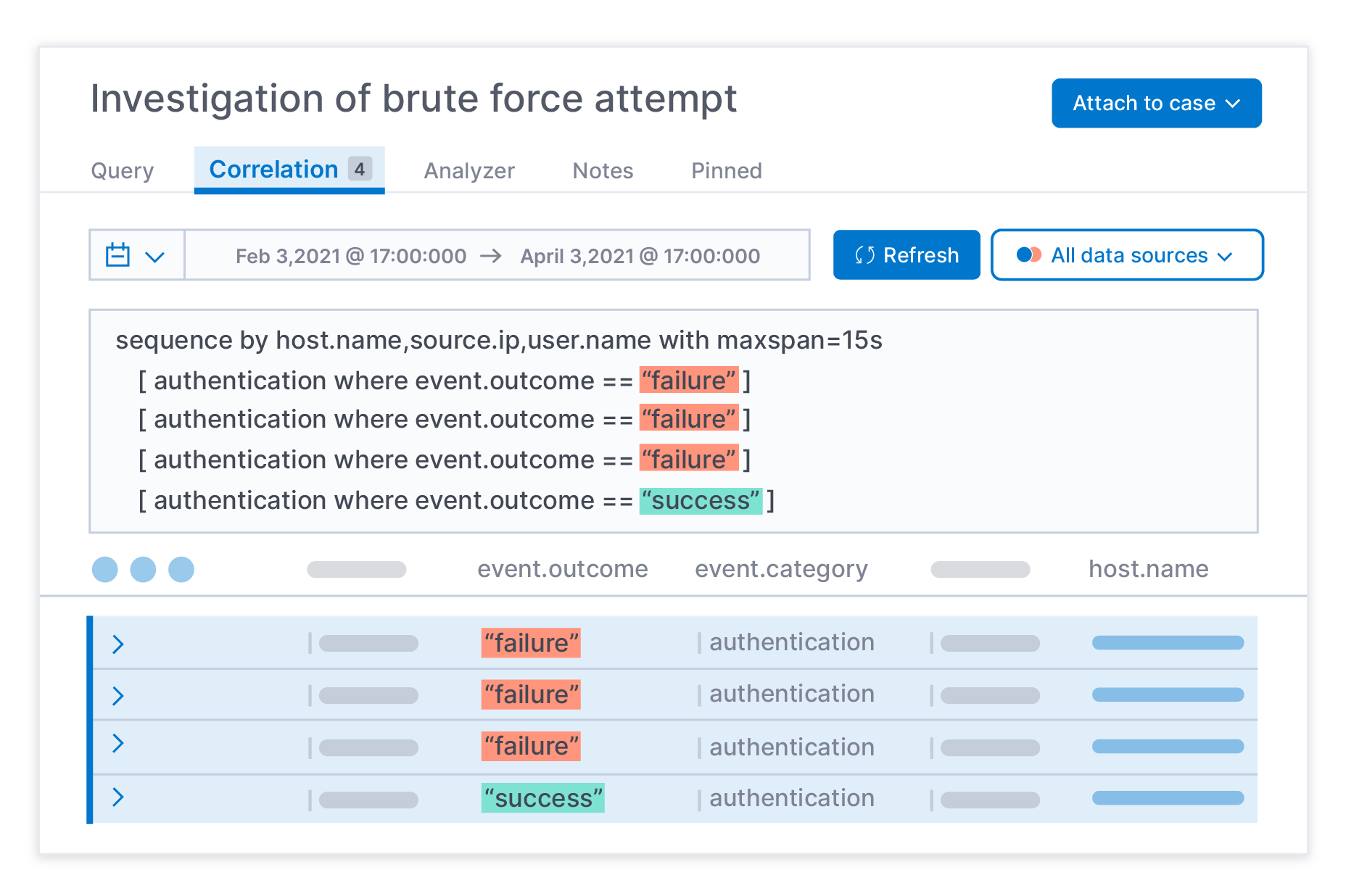
Accelerate hunting and investigation with analyst-driven correlation using EQL.
Analyst-driven correlation, new in Elastic Security 7.12, is a critical tool for practitioners who need to turn data into information and insight. It equips analysts to hunt and investigate threats more quickly by revealing the relationships between key data, rather than inundating analysts with a flood of decontextualized data points. This results in more targeted hunting and investigation, with higher-fidelity detections derived from the findings that analysts uncover during those investigations.
Analyst-driven correlation is driven by Event Query Language (EQL), the technology behind advanced correlation in the Elastic Security detection engine. Putting the power of correlation in practitioner hands streamlines SecOps workflows and helps uncover attack progression, making sequence-based analysis — across all data, no matter the source — as simple as search. All from the hunting and investigation workspace in Elastic Security.
Slow response times have traditionally hampered attempts to boost threat hunting and investigation with correlation. Now, with Elastic Security, practitioners can surface meaningful data at the speed of Elasticsearch. And with the ability to apply correlations across historical data, analysts can glean key insights from the most patient and sophisticated of adversaries — in just minutes. Security teams benefit from multiple detection and investigative methods that cover a broad range of security use cases. Combining EQL-based correlations with machine learning-based detections, indicator match type detection rules, and third-party context at cloud scale enables a more comprehensive security strategy.
Analyst-driven correlations in Elastic Security.
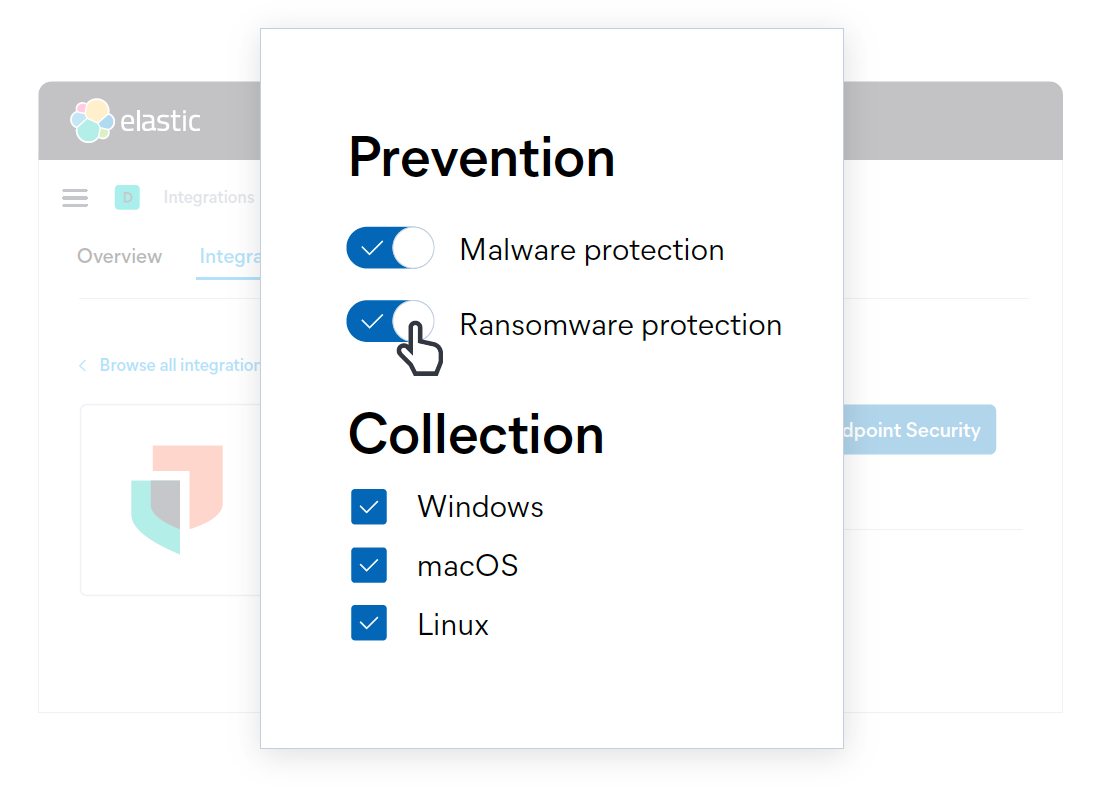
Stop ransomware with behavioral analysis, now in the Elastic Agent.
Ransomware attacks continue to prove profitable and the techniques they employ are evolving quickly. Fortunately, like other forms of malware, ransomware can be stopped at several points along the attack chain. Enter defense-in-depth.
Elastic Security 7.12 introduces a new layer of ransomware prevention: behavioral analysis with the Elastic Agent, complementing the signatureless anti-malware first introduced in Elastic Security 7.9. Behavioral ransomware prevention on the Elastic Agent detects and stops ransomware attacks on Windows systems by analyzing data from low-level system processes, and is effective across an array of widespread ransomware families — including those targeting the system’s master boot record.
Expanded ransomware protection in Elastic Agent.
Get all the details in the Elastic Security 7.12 blog.
There’s always more...
So much more. Check out the individual solution and product blog posts for the details on everything we added in 7.12:
Elastic Stack
Elastic Cloud
What’s new in Elastic Cloud for 7.12?
Elastic Solutions
Elastic Enterprise Search 7.12 released
Elastic Observability 7.12 released
Elastic Security 7.12 released
Get started with a free trial on Elastic Cloud.
The release and timing of any features or functionality described in this document remain at Elastic’s sole discretion. Any features or functionality not currently available may not be delivered on time or at all.

