

What is data security?
Data security definition
Data security is the process through which an organization protects its digital information from unauthorized access, use, modification, corruption, exploitation, loss, and theft. It is an essential component of cybersecurity that involves implementing tools and measures to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data.
As cyber threats continue to evolve and multiply globally, data protection is critical. Organizations need data security to protect their corporate and customer data, intellectual property, financial information, and other valuable digital assets from attack.
Common types of sensitive data that require security measures include:
- Personally Identifiable Information (PII), including names, addresses, phone numbers, social security numbers, and DOBs
- Financial data, including bank account numbers and credit card information
- Intellectual property, including patents, trade secrets, and copyright and trademark material
- Health information, including medical records, patient data, and prescription information
- Confidential business information, including sales and pricing data and strategic planning
Why is data security important?
Inadequate data security can come with serious consequences, both financially and reputationally. The average cost of a data breach for US companies has now surpassed $9.44 million1, and 83% of organizations1 have had more than one breach. Organizations are exposed to legal liability and potentially devastating financial losses. And highly visible breaches can significantly damage brand perception, resulting in a loss of customer trust.
In the past decade alone, data breaches have affected many of the world’s most prominent companies. Recent data security breaches have targeted giants such as Apple, Meta, Twitter, and more, highlighting the need for data protection across the board. In 2021, a data breach at T-Mobile impacted an estimated 77 million people — listing customer data on a known cybercriminal forum and resulting in a $350 million settlement.2 Current data security trends aim to reduce the impacts — and costs — of security breaches.
Types of data security measures
There are several common types of data security measures that organizations implement to protect their sensitive data. Broadly categorized, they include:
- Encryption
Encryption is the process of converting data into an encoded format that can only be read and deciphered by authorized parties with a secret key or password. The goal is to make it nearly impossible for bad actors to access sensitive information, even if they manage to breach the security measures protecting it. - Access controls
Access controls are measures organizations can take to guarantee that only those who are properly authorized to access certain levels of data and resources are able to do so. User verification and authentication methods can include passwords, PINs, biometrics, and security tokens. - Firewalls
Firewalls are network security mechanisms that monitor and control incoming and outgoing traffic, shielding your system from harm. By filtering out unauthorized traffic, firewalls help prevent hackers and other cybercriminals from gaining access to an organization's data. - Antivirus software
Antivirus software is designed to detect, remove, and quarantine malware, viruses, and other malicious software that threatens to compromise your systems and data security.
Legal and regulatory requirements
Robust data security measures help protect against cyber threats that can lead to breaches, including hacking, phishing, ransomware, and malware attacks. They can also assure compliance with a constantly evolving set of legal and regulatory requirements across industries and the world, including:
- Europe’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
- California Consumer Protection Act (CCPA)
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)
- Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS)
Failing to follow regulations can result in hefty fines, legal penalties, and loss of trust. Investing in effective data security isn't just about checking boxes — it's about safeguarding your organization’s most valuable assets for the future. The ideal solution will meet both your overall security needs and your compliance requirements.
Best practices for data security
A comprehensive data security strategy involves deploying multiple tools, technologies, and processes. Advanced solutions like data encryption, masking, redaction, and erasure are also commonly used.
The first step is to identify and classify your organization’s sensitive data. Then, establish a clear policy for data governance that defines criteria for access and proper use. Once you have a firm handle on your critical data — including where it is, who has access to it, what they can use it for, and why — you’re far better positioned to implement security solutions.
It’s also important to remember that sometimes threats are internal. Whether intentional or not, human error is frequently a culprit in embarrassing data leaks and breaches. This makes rigorous employee training a must.
From a cybersecurity perspective, here are some critical best practices for data security we recommend adopting:
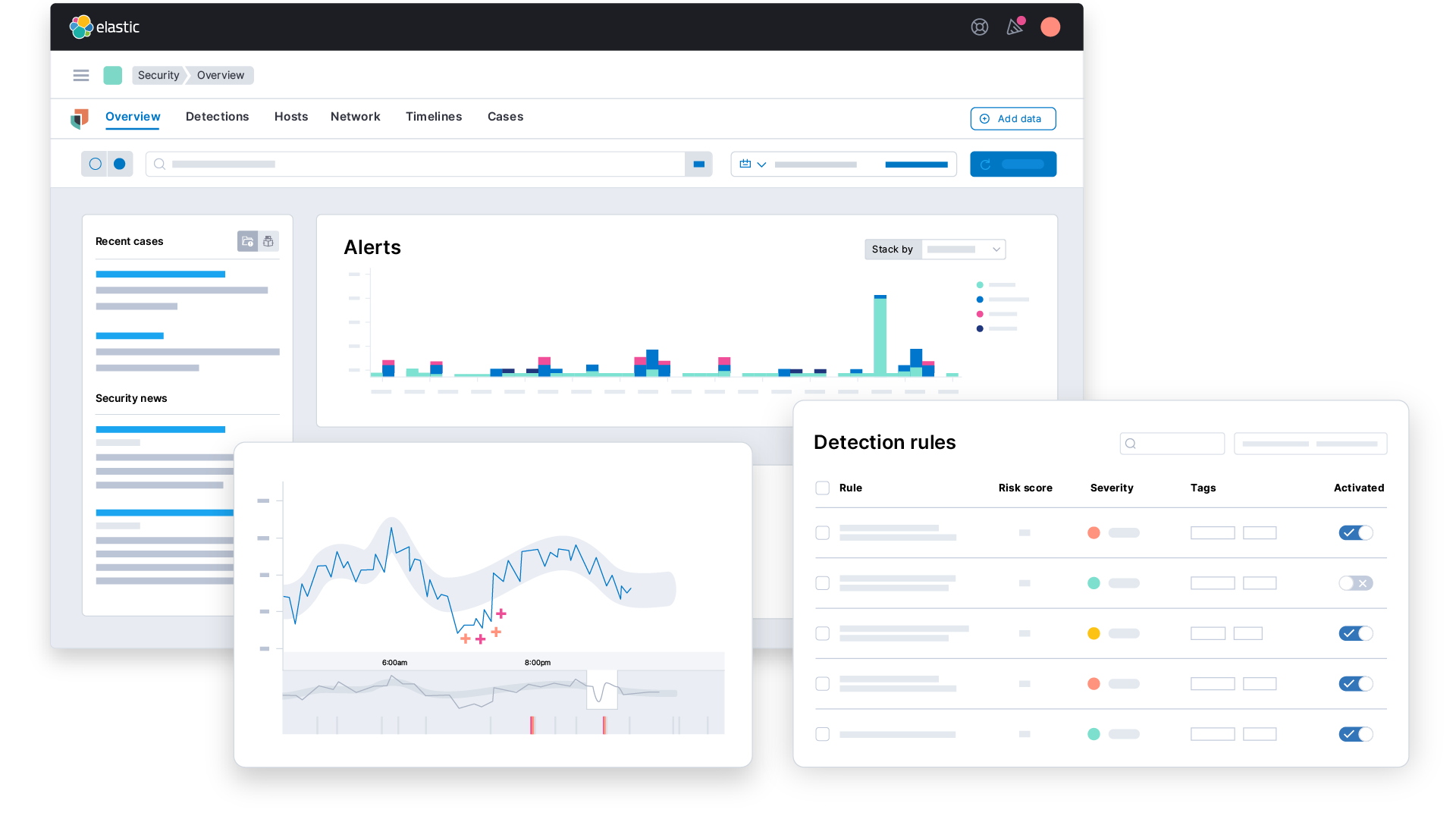
Security information and event management (SIEM)
Security information and event management (SIEM) is a cybersecurity solution used to detect and respond to threats within an organization. A SIEM platform works by collecting log and event data and providing security analysts with a comprehensive view of their IT environment.
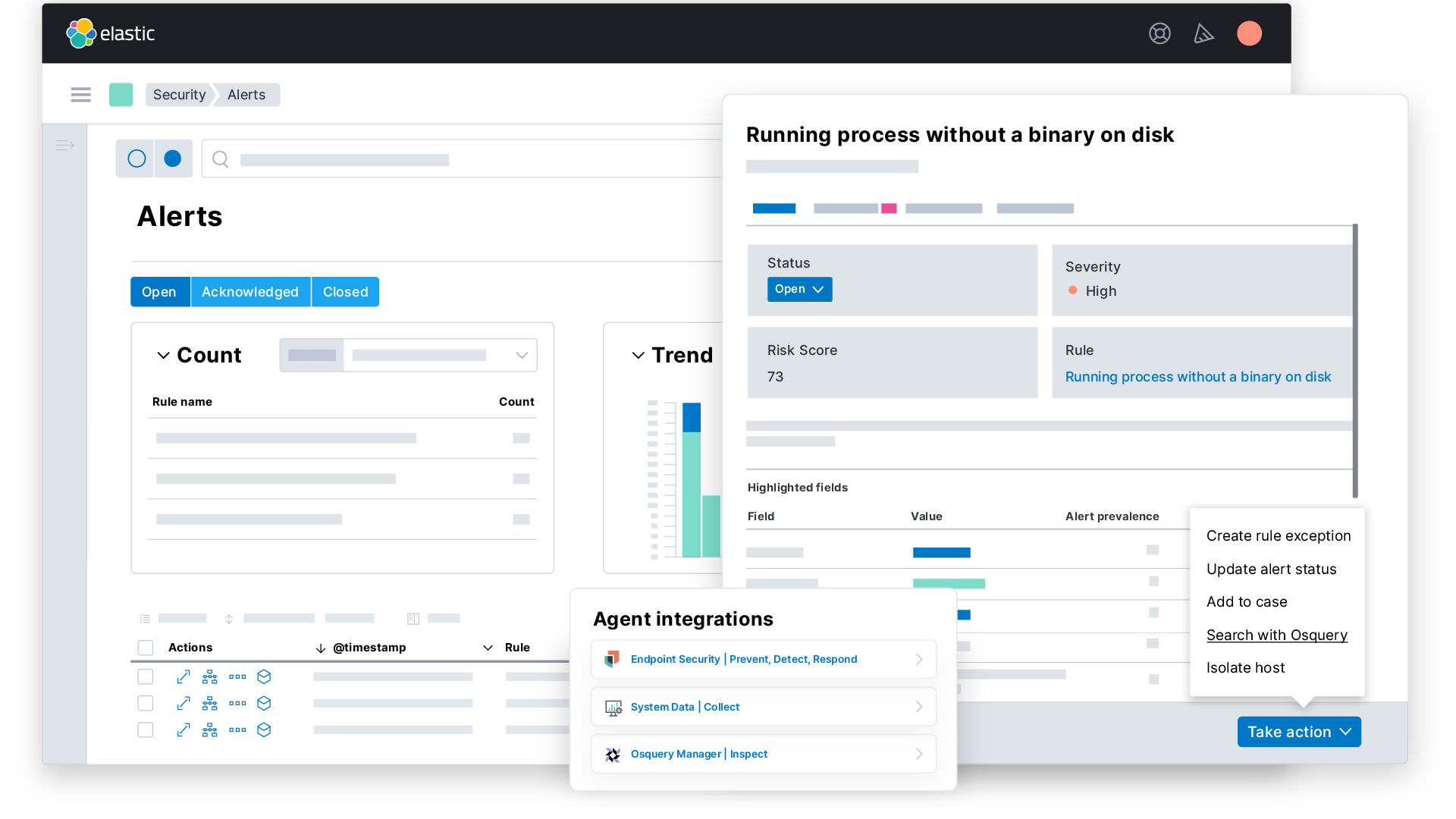
Endpoint security
Endpoint security is the practice of protecting the devices that connect to a network, such as laptops, servers, and mobile devices, with the goal of preventing ransomware and malware, detecting advanced threats, and arming responders with vital investigative context.
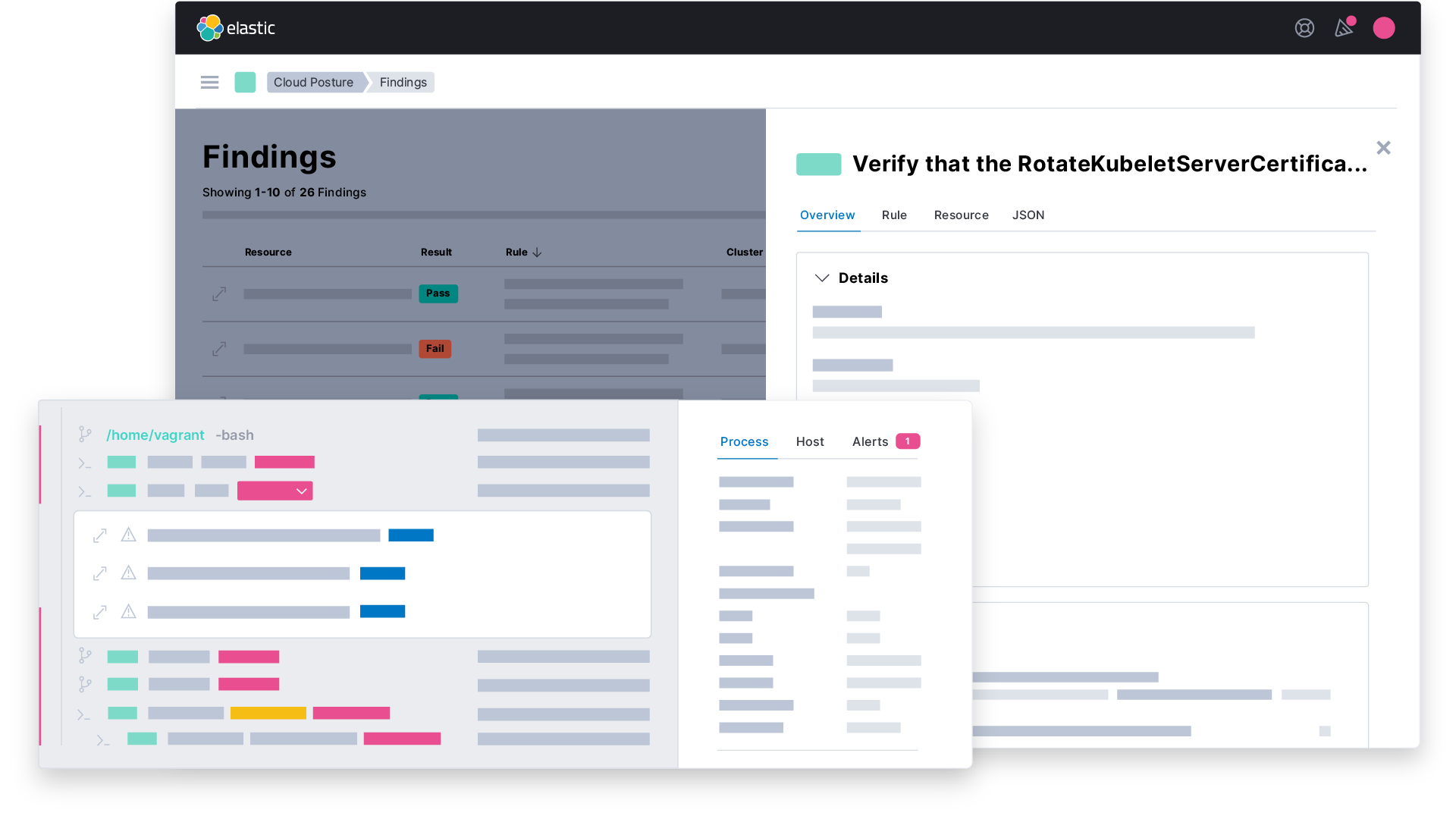
Cloud security
Cloud security is the practice of protecting cloud technologies from misconfigurations and breaches. The right cloud security solution will protect cloud deployments by providing rich visibility into cloud posture. It will protect cloud workloads with prevention, detection, and response capabilities — all in one integrated solution.
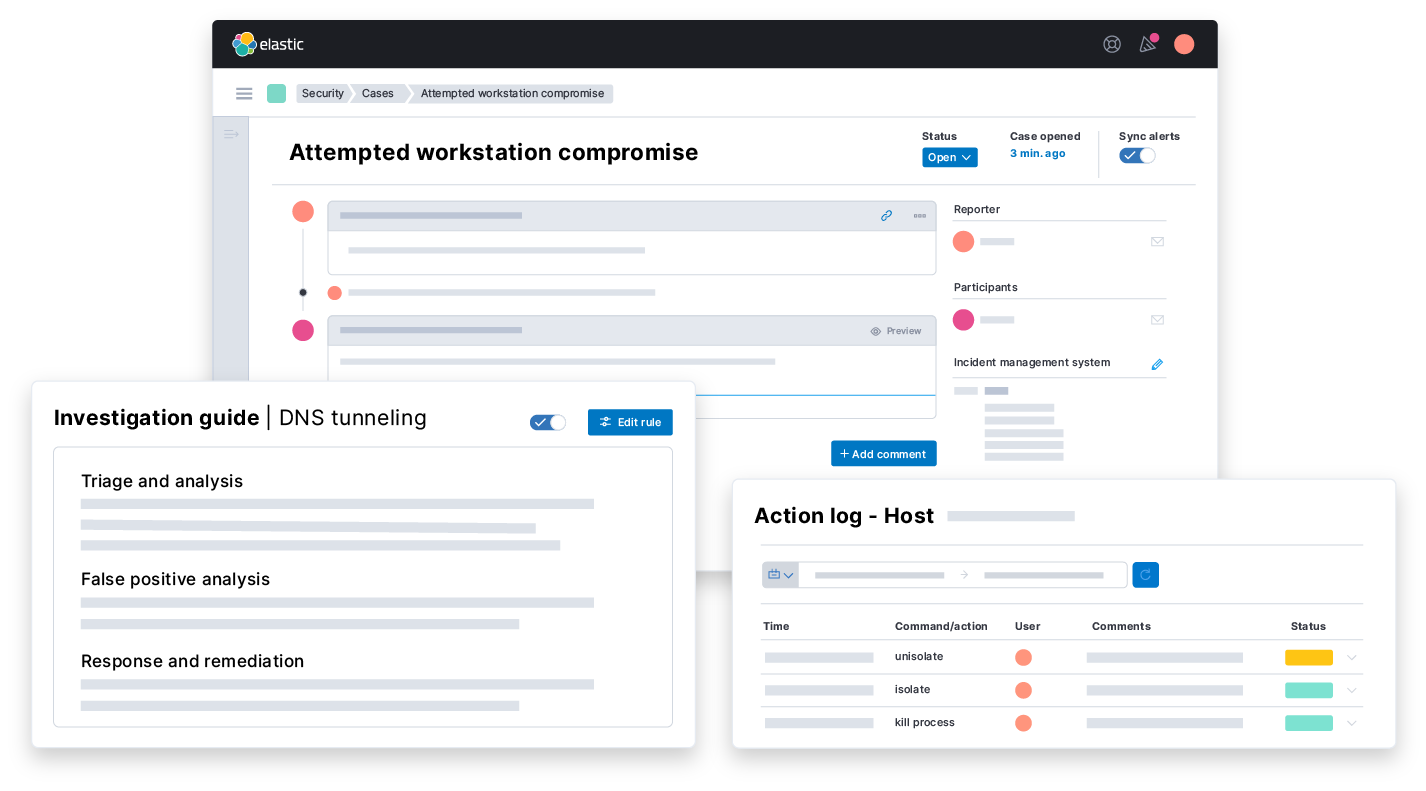
Security orchestration, automation, and response (SOAR)
Security orchestration, automation, and response (SOAR) enables security teams to standardize and streamline their organization’s response to cyber attacks and incidents.
Extended detection and response (XDR)
XDR, or extended detection and response, is a cybersecurity tool for threat detection and response that collects and correlates data from various sources across the IT environment to provide a cohesive, holistic approach to security operations systems.
Application security
Application security is the practice of protecting applications, whether running in the cloud, on on-prem servers, or on client devices. Proper application security ensures that data within applications is secure and won’t be stolen.
Network security
Network security focuses on protecting network infrastructure from misuse, deploying tactics and strategies including firewalls, intrusion prevention/detection systems, network segmentation, and VPNs.
Threat intelligence
Threat intelligence helps security teams protect against cyber attacks by analyzing collected data to provide insights into attackers’ activity, tactics, and targets.
Identity and access management
Identity and access management, often known as IAM, are the frameworks and technologies used to manage digital identities and user access, including two-factor and multifactor authentication and privileged access management. They are particularly effective when combined with Zero trust, a cybersecurity framework that requires all users to be authenticated before they can access data, applications, and other systems.
Future trends of data security
The world of data security is by necessity in a constant state of evolution, and the best IT teams not only stay ahead of the latest threats and vulnerabilities, they stay informed about the emerging trends and technologies in the field. With the proliferation of data and the increasing complexity of the systems that help create, utilize, and store it — along with rapid cloud adoption and the unprecedented number of workers who need remote access — the threats to data security will only multiply.
Organizations around the world are investing heavily in the future of data security. Here are some important trends in the industry to be aware of:
- Authentication trends
The use of multi-factor authentication (MFA) will only continue to grow, with users being required to provide several forms of identification to access a system beyond a password, including security tokens, fingerprints, and other biometrics like facial recognition or iris scanning. - Privilege trends
The principle of least privilege (PoLP) limits user access to only the data and systems necessary for performing one’s job duties. Unnecessary privileges that could potentially be exploited by cybercriminals will become increasingly rare, as organizations effectively limit the damage that can come from compromised accounts, insider threats, and phishing and malware attacks. - Analytics trends (Artificial Intelligence)
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are at the forefront of analytics trends in cybersecurity, with systems increasingly able to automatically detect and prevent threats and detect anomalies in real time. Behavior-based analytics based on machine learning are also able to detect suspicious user activity. - Cloud security trends
As more organizations move their data and applications to the cloud, ensuring the security of cloud environments will be paramount. In addition to cloud access security brokers (CASBs), one of the emerging technologies is the Cloud Native Application Protection Platform (CNAPP). CNAPP provides a comprehensive set of security controls for cloud-native applications, including container-based applications and microservices, helping organizations secure their cloud-native applications by providing features such as runtime protection, vulnerability management, and compliance management. Elastic offers an integrated approach combining security analytics with CNAPP.
Protect your organization’s data with Elastic
Elastic offers many of the aforementioned security use cases within a unified, integrated solution, allowing security analysts to take on advanced cybersecurity tasks across the same interface. Our advanced enterprise search capabilities eliminate blind spots, adding a crucial layer of cybersecurity. And Elastic provides a full-stack view of what’s going on in your network, so you can identify and address vulnerabilities — quickly and at scale.
We help organizations prevent, detect, investigate, and respond to data security threats, keeping your vital business and customer information safe. Naturally, this applies to your Elasticsearch data. Elastic Security can help you:
Protect: Automated detection of ransomware and malware, including prebuilt rules and prebuilt ML jobs for data security use cases. Security features to protect information and manage access to resources, including role-based access control.
Investigate: We enable comprehensive monitoring of activity within your environment and deep visibility for host and cloud, including file integrity monitoring.
Respond: Respond faster with complete context and powerful search capabilities. With Elastic, analysts have everything they need to be more productive and prevent reputation-damaging attacks. And automated response actions, like remote host isolation, quarantines attacks to prevent them from getting into your network.
Elastic Security is an integrated security solution that delivers unlimited visibility, reduced investigation times, out-of-the-box protections, customizable analyst workflows, deep contextual insights, and a pay-as-you-grow adoption model.
Stay ahead of data security threats and try Elastic Security for free.
Data security resources
- Elasticsearch security: Best practices to keep your data safe
- Elastic APM Guide: Data security
- Customer trust relies on building IT systems that scale
- Cybersecurity is a data challenge, and better search technology is key to improving visibility and action
- Elasticsearch security: Best practices to keep your data safe
Footnotes
1 IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report 2022
2 "T-Mobile Reaches $500 Million Settlement in Huge 2021 Data Breach," New York Times, Jul 22, 2022