Elasticsearch: Build a chatbot RAG app
Overview
Introduction
In this guide, you'll get started on setting up and running a chatbot RAG app. RAG stands for retrieval augmented generation. It is a method of using a custom data source to ground the responses from generative AI (GenAI) large language models (LLMs) to prevent problems like LLM hallucinations. This journey walks through the process of how to configure and run Elastic's example chatbot RAG app so you can see it in action for yourself.
This chatbot RAG app is open source and hosted on GitHub so you can clone it, fork it, and create your own version of it. The app uses Elastic Cloud to host an Elasticsearch index that serves as the retrieval augmentation "source of truth" for the RAG app. This ensures that the responses it generates are based on the information in the documents contained within the index. The chatbot app is coded to support the multiple popular LLM services like OpenAI. The architecture of the app is based on a Python Flask backend and a React frontend. See the app’s complete list of requirements in the Elasticsearch Labs chatbot tutorial.
The chatbot RAG app is a great way to learn and experiment with RAG apps because you can run it on your local computer and see firsthand how integrations with Elastic Cloud and LLMs work together to create a GenAI powered search experience that is customized to your unique set of documents. The app supports integration with a variety of LLMs like OpenAI, AWS Bedrock, Azure OpenAI, Google Vertex AI, Mistral AI, and Cohere. There are two ways to deploy the example chatbot RAG app on your local computer: using Docker or Python.
Let's get started
Running the chatbot RAG app
Follow the steps in either the Run the chatbot app with Docker or the Run the chatbot app with Python sections below depending on your preferred deployment approach. Using Docker requires fewer steps, while using Python will provide a more in-depth understanding of how to configure and run the backend and frontend components of the app. Both ways of running the app use OpenAI as the LLM. Once you've got the app running with OpenAI, updating the app to use one of the other supported LLMs requires minimal steps.
Run the chatbot app with Docker
The process of running the chatbot RAG app with Docker involves:
- Cloning the app's code
- Creating an Elastic Cloud deployment
- Creating an OpenAI API key
- Populating the app's settings
Follow this a guided tour that includes every step required to get you to the goal of running the app on your local computer:
Guided tour: Run the chatbot RAG app with OpenAI using Docker
Run the chatbot app with Python
The process of running the chatbot RAG app with Python involves:
- Cloning the app's code
- Creating an Elastic Cloud deployment
- Creating an OpenAI API key
- Populating the app's settings
Once the app and its dependencies are configured, the app's Python backend will be started. Then, React frontend will be started to provide the app's UI, which you'll be able to interact with in your browser.
Follow this guided tour that includes every step required to get you to the goal of running the app on your local computer:
Guided tour: Run the chatbot RAG app with OpenAI using Python
Working with Elasticsearch
Play with the running app
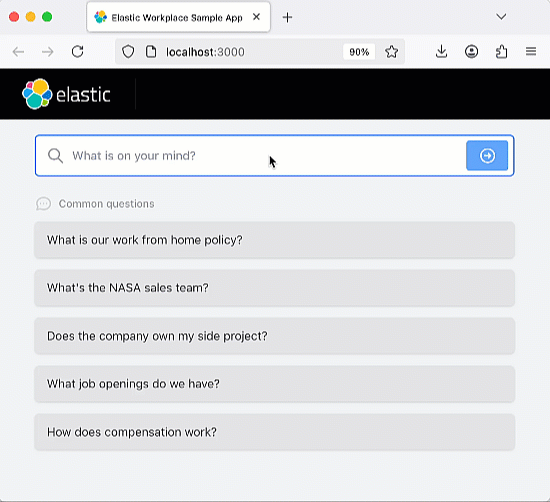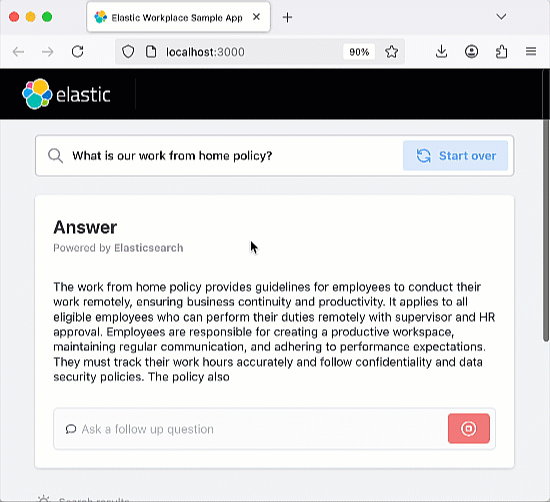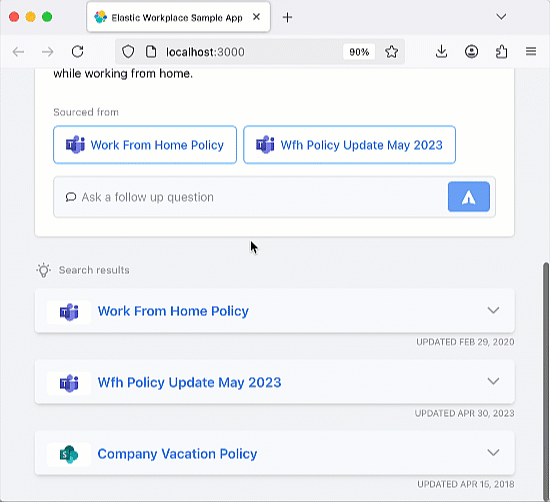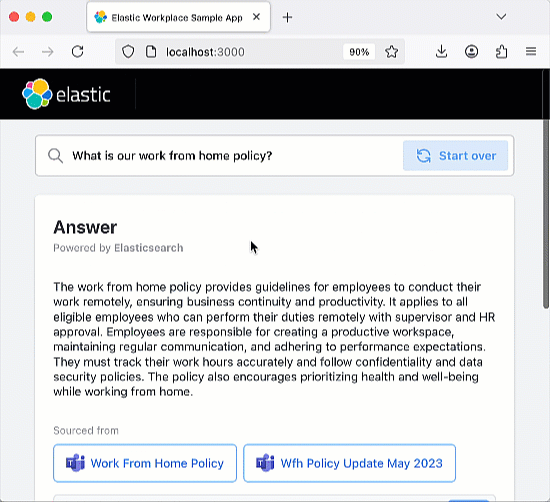
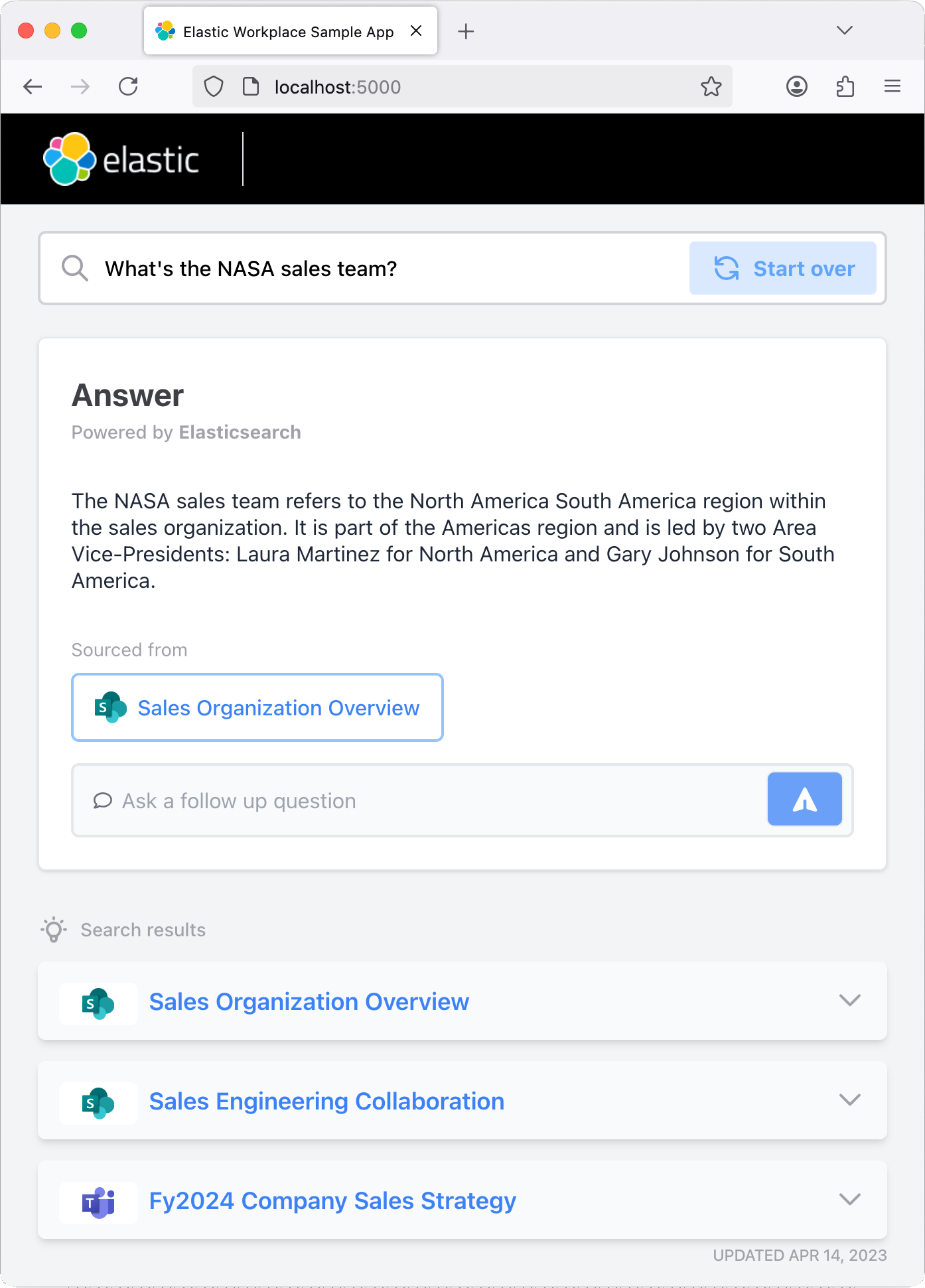
Once you have the app running, go ahead and try asking a question or using one of the preset questions. The app is coded to include an Elastic index that ingests the history of your chats, so you should try asking follow-up questions that test the "memory" of the chatbot.
Next steps
Thanks for taking the time to learn about the process of running the Elastic chatbot RAG example app. As you begin your journey with Elastic, understand some operational, security, and data components you should manage as a user when you deploy across your environment.
Ready to get started? Spin up a free 14-day trial on Elastic Cloud.